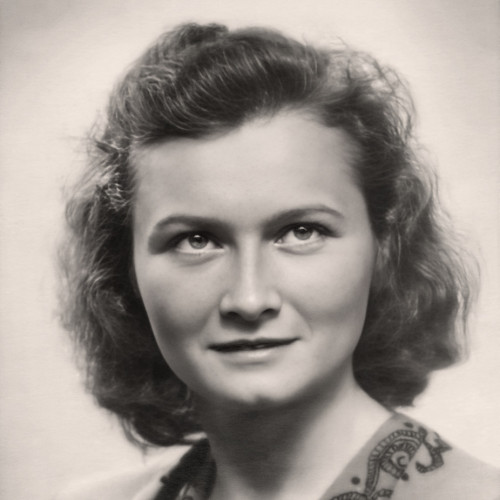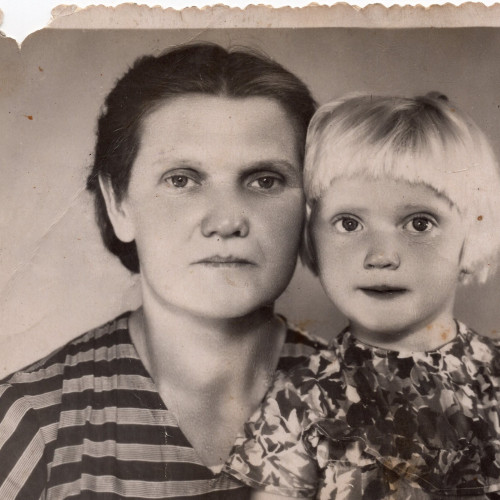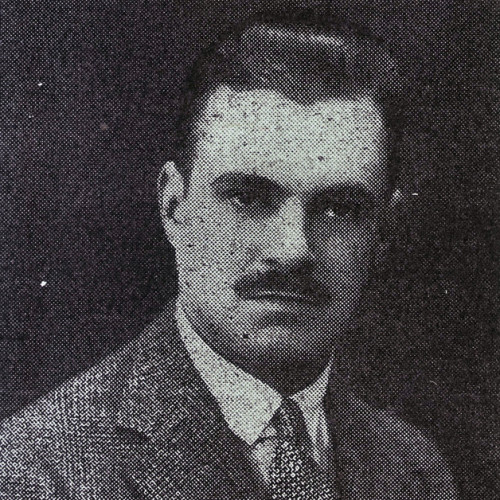Recipients - Instytut Pileckiego
Awarded in 2024
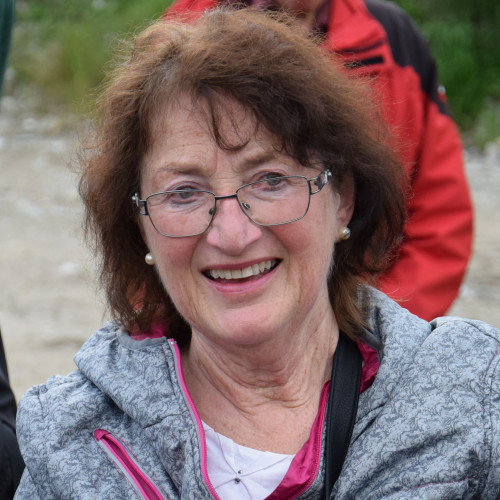
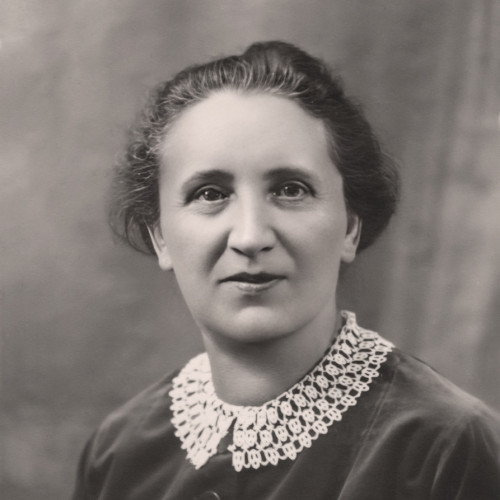
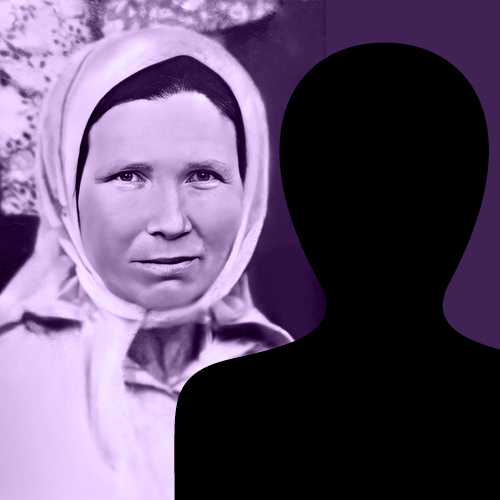
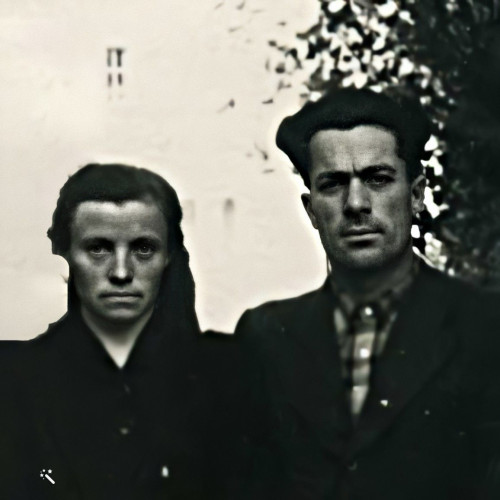
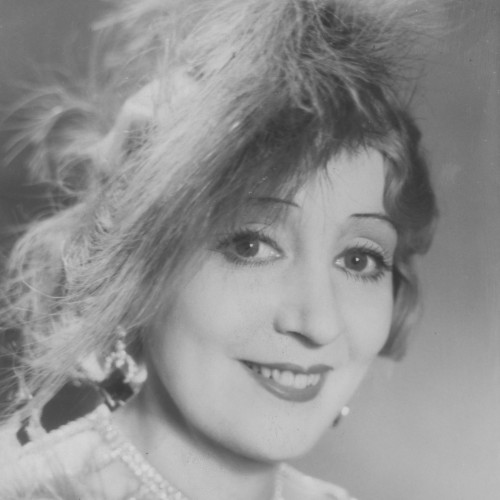
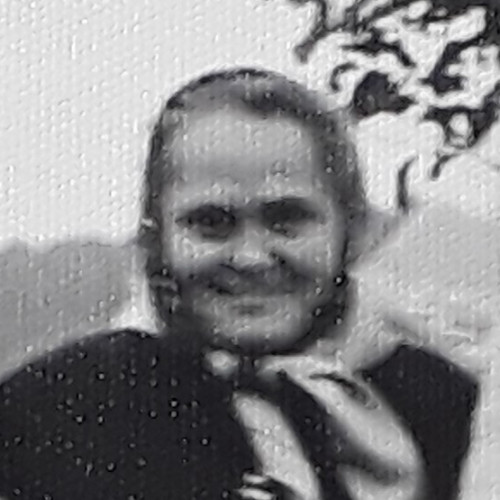
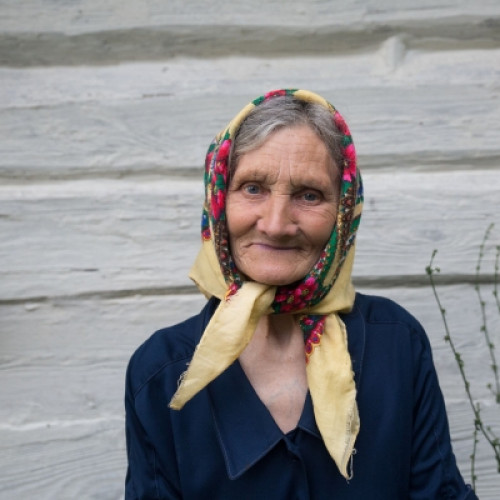
- Martha Gammer (1947)

awarded
Martha Gammer (1947)
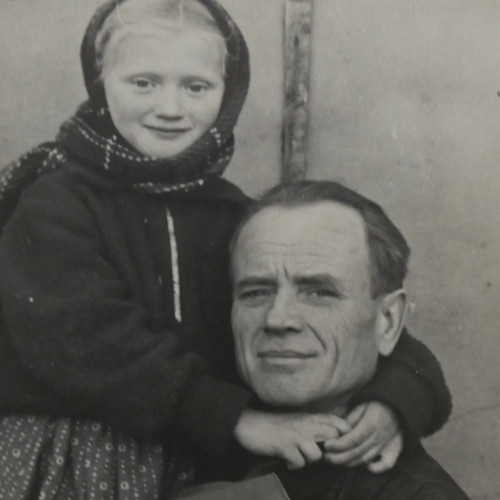
In the 1970s, few people knew that the tunnels excavated in the hills near Gusen were the result of slave labor by prisoners of the German Nazi concentration camp that existed there during the Second World War.
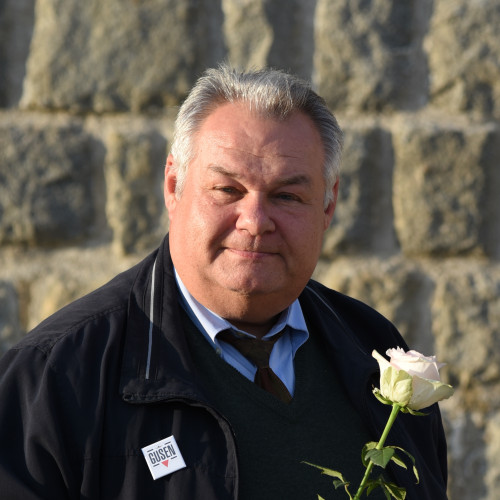
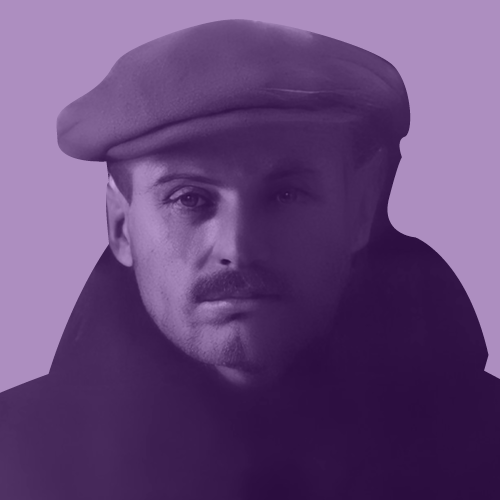
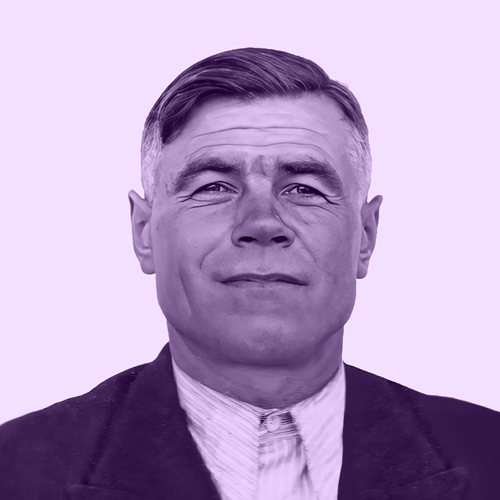
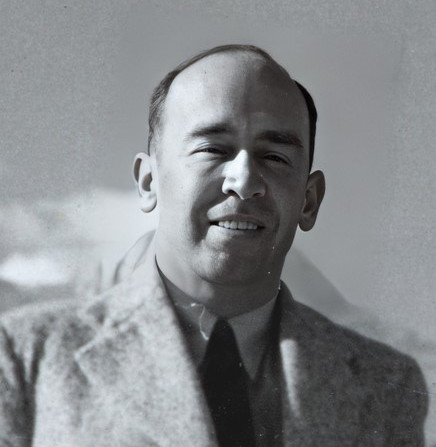
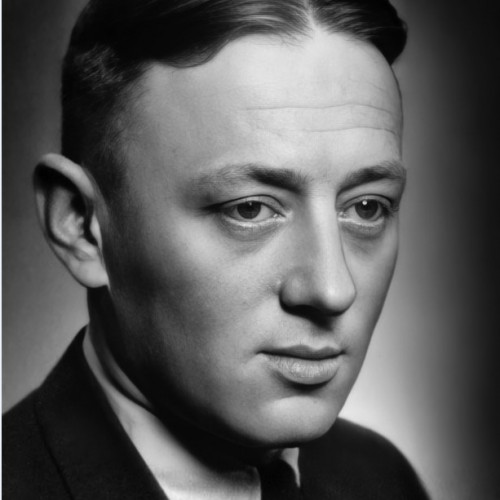
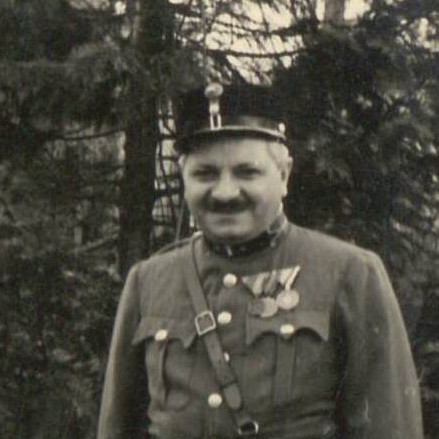
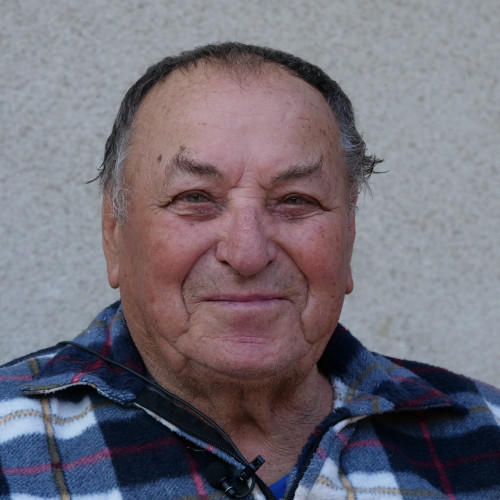
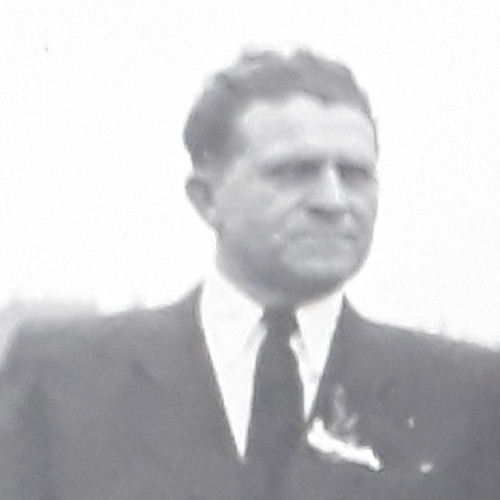
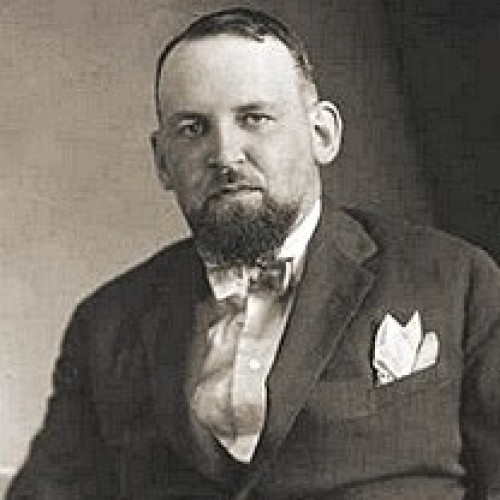
- Rudolf Haunschmied (1966)

awarded
Rudolf Haunschmied (1966)
As a six-year-old boy growing up near Gusen, Rudolf Haunschmied learned that during the Second World War the village had been the location of a German Nazi concentration camp.
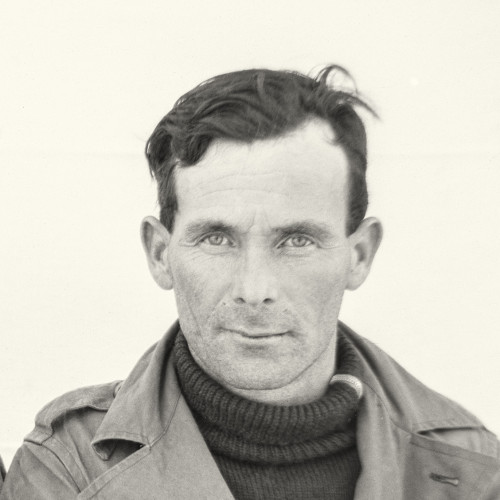
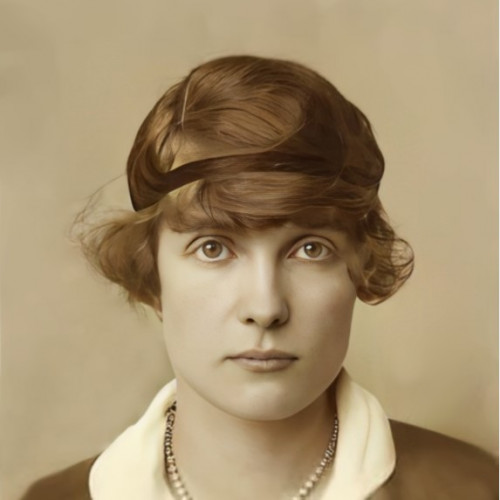
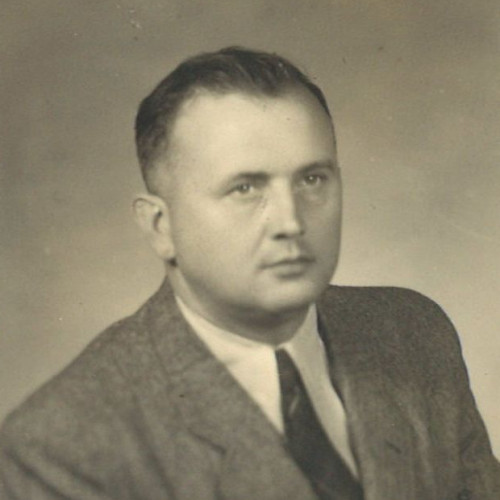
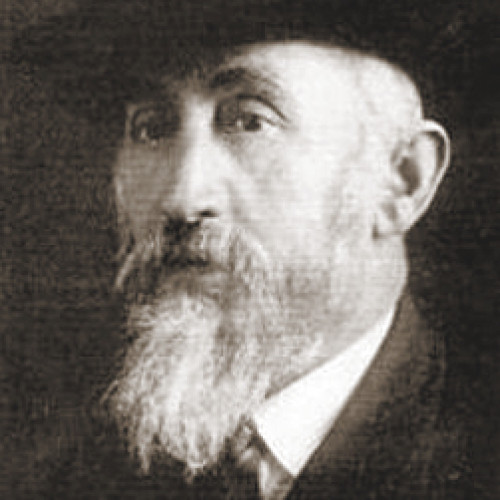
- Alfred Iversen

awarded
Alfred Iversen
(1908–1987)A Norwegian citizen who helped Poles, prisoners of a German forced labor camp, escape to Sweden.
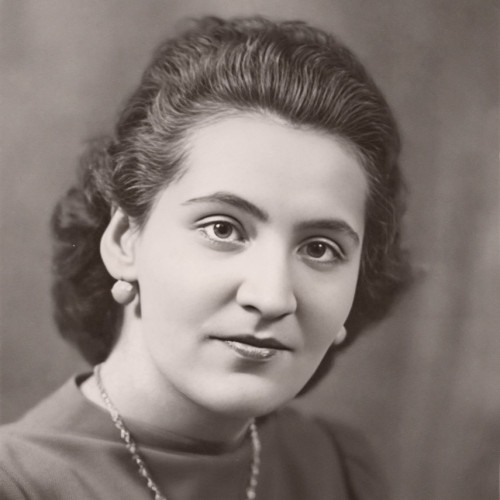
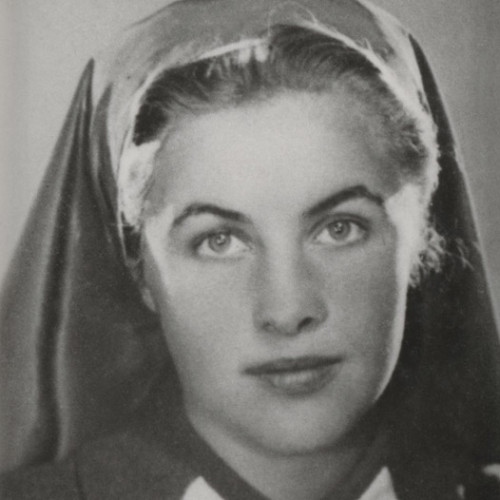
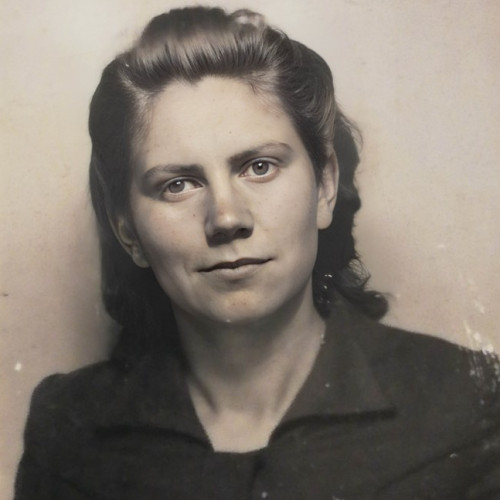
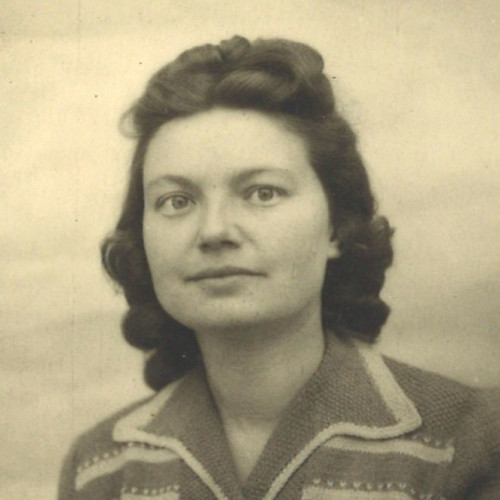
- Etela Laczuschová

awarded
Etela Laczuschová
(1922–1944)The Kežmarok house was a unique location for Polish couriers and refugees: they could rest and recuperate there, eat a meal, or obtain necessary assistance.
- Ferdinánd Leó Miklósi

awarded
Ferdinánd Leó Miklósi
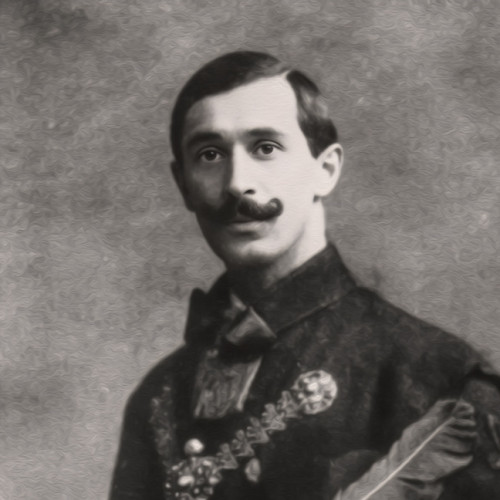
(1889–1968)As a 21-year-old in 1910, he was a member of the Hungarian delegation that participated in the unveiling of the Grunwald Monument in Kraków.
- Berta Ludvighová (1903–1983) Otto Ludvigh (1898–1987)

awarded
Berta Ludvighová (1903–1983) Otto Ludvigh (1898–1987)
The Kežmarok house was a unique location for Polish couriers and refugees: they could rest and recuperate there, eat a meal, or obtain necessary assistance.
- Aud Valla

awarded
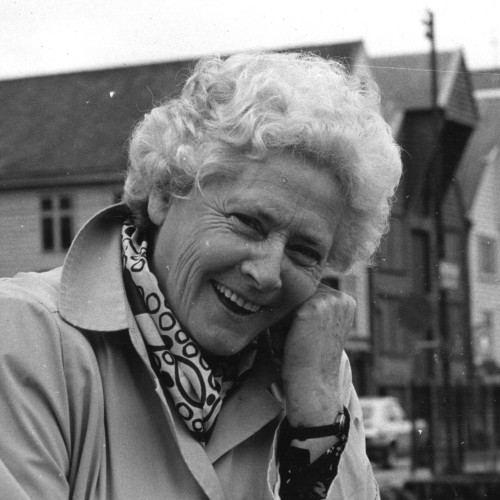
Aud Valla
(1922–2014)Aud Sejlelid, still going by her maiden name at the time, spent her entire life in the small town of Hemnesberget in northern Norway, in a picturesque land of fjords.
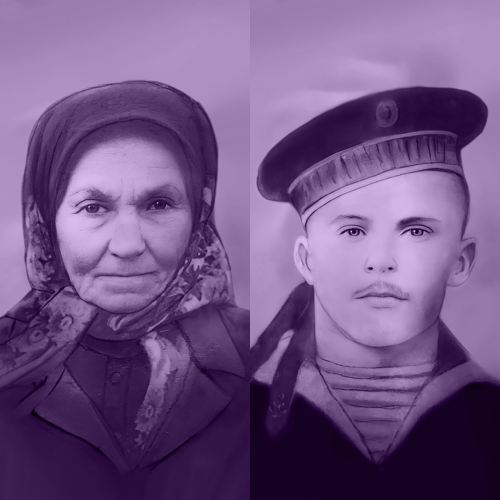
- Helena Vargová

awarded
Helena Vargová
(1891–1974)The Kežmarok house was a unique location for Polish couriers and refugees: they could rest and recuperate there, eat a meal, or obtain necessary assistance.
- Svensson Bernacka Walborg

awarded
Svensson Bernacka Walborg
(1921–2005)Her first contact with Poles dated back to the Second World War, when she was helping prisoners of the German labor camp in Sandnes, a city located less than 16 kilometers from Stavanger.
Awarded in 2023
- Semen Biliczuk

awarded
Semen Biliczuk
(1890–1944)Jews, Ukrainians, Poles – the population of the prewar village of Kisielin [now Kysylyn] [now Kysylyn] was characterized by a vivid mosaic of ethnic and religious groups. The leader of such a community had to be able to find a common ground with everyone.
- Oksana Karpiuk (1892-?)

awarded
Oksana Karpiuk (1892-?)
Oksana found the children at nightfall. She hid not only the youngest members of the Polish family at her home, but also the elderly – the parents and the grandmother.
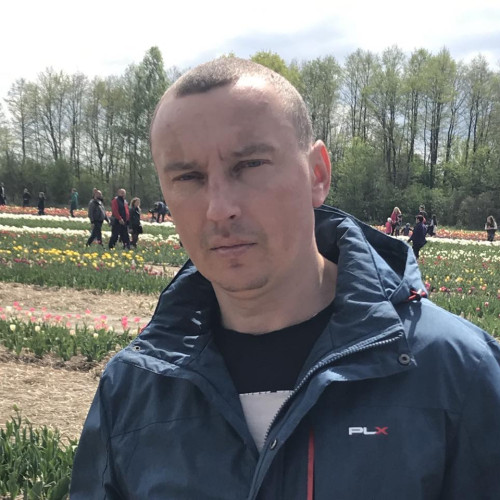
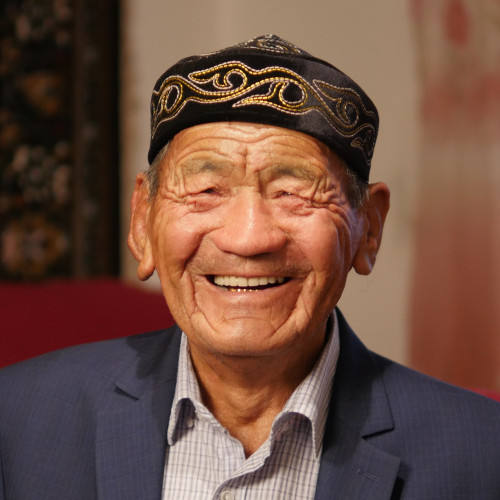
- Wołodymyr Kryżuk

awarded
Wołodymyr Kryżuk
Since the early 2000s, he has been helping Poles who travel to look after the graves of the victims of the massacre carried out by members of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army (faction of the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists).
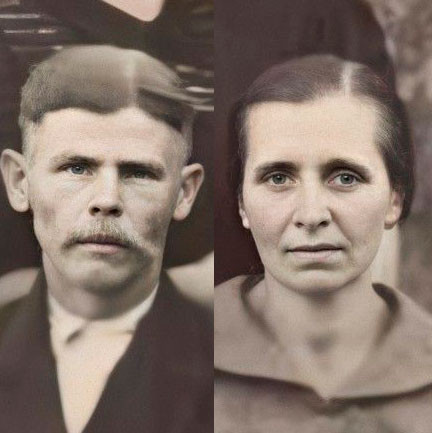
- Anton Parfeniuk (1890–1947) Lubow Parfeniuk (1903–1967)

awarded
Anton Parfeniuk (1890–1947) Lubow Parfeniuk (1903–1967)
The Parfenyuks produced the best cottage cheese and cream in Kisielin. The land of Volhynia had been especially favorable to them, and, in addition to milk and dairy products, the family also traded in agricultural produce.
- Anastasija Koreń (1908–1967) Mykoła Koreń (1905–1944)

awarded
Anastasija Koreń (1908–1967) Mykoła Koreń (1905–1944)
On the evening of 15 July, Mykola’s brother-in-law appeared at the Korens’ doorstep, accompanied by four children of their neighbors, the Adamowiczs: nine-year-old Teresa, five-year-old Janusz, three-year-old Stasia and one-and-a-half-year-old Henio.
- Paraskewa Padlewska

awarded
Paraskewa Padlewska
(1888–1960)“Housewife” – the official term used to describe women who were not gainfully employed does not reflect the resourcefulness which Paraskeva Padlevska displayed.
- Piotr Parfeniuk

awarded
Piotr Parfeniuk
(1904–1993)Although his given name was Petro, Parfeniuk used the name Piotr for the majority of his long life. Before the outbreak of the war, he met his future wife, Stanisława, from the Polish Czerwinek family.
- Sofia Kyc (1890–?) Pawło Kyc (1897–?)

awarded
Sofia Kyc (1890–?) Pawło Kyc (1897–?)
Pavlo Kyts had no doubts – their Polish neighbors were in grave danger. On the evening of 15 July, Pavlo decided to help two neighboring families.
- Jewhenia Bondaruk (1922–ok. 1995) Prokop Bondaruk (1918–2001)

awarded
Jewhenia Bondaruk (1922–ok. 1995) Prokop Bondaruk (1918–2001)
Yevhenia and Prokop Bondaruk lived near Yevhenia's mother, Oksana Karpiuk, and provided shelter not only to the youngest members of the Polish Adamowicz family, but also to their parents and grandmother.
- Sawa Kowtoniuk (1888–ok. 1970) Ustyna Kowtoniuk (1895–ok. 1980)

awarded
Sawa Kowtoniuk (1888–ok. 1970) Ustyna Kowtoniuk (1895–ok. 1980)
The Kovtoniuks gave shelter to several families: the Sławińskis, Romanowskis, Maciaszeks, and the Okólskis.
- Herasym Łukiańczuk

awarded
Herasym Łukiańczuk
(1890–1953)“He walked slowly and told me discreetly: ‘Don’t go anywhere, maybe they won’t see you. I will come and get you in the evening. Your brother is already at my place,’” recalled Leokadia Skowrońska, who was saved by Herasym Lukianchuk.
Awarded in 2022
- Ilona Andrássy de Csíkszentkirály et Krasznahorka

awarded
Ilona Andrássy de Csíkszentkirály et Krasznahorka
(1917–1990)Following the outbreak of the Second World War, Ilona Andrássy was working together with other aristocrats, established the Hungarian-Polish Refugee Welfare Committee in Budapest.
- Erzsébet Szápáry (1902-1980) Antal Szápáry (1905-1972)

awarded
Erzsébet Szápáry (1902-1980) Antal Szápáry (1905-1972)
Erzsébet and Antal Szápáry came from a famous family of Hungarian aristocrats. Their mother, Maria Przeździecka, was a Pole, and this fact had a bearing on their involvement in relief activities for Polish refugees after 1939.
- Julien Bryan

awarded
Julien Bryan
(1899–1974)On 16 September 1939, the Polish Radio broadcast the following appeal: “President Roosevelt and the people of America! I speak from the besieged city of Warsaw, Poland. My name is Bryan – Julien Bryan, American photographer.
- Pedro Correia Marques

awarded
Pedro Correia Marques
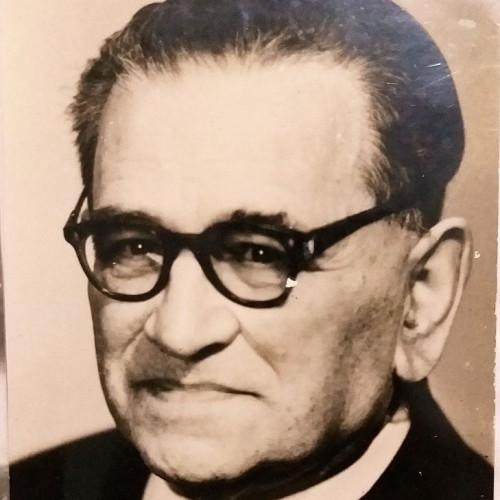
(1890–1972)It began with penning short articles and tidying the editorial office of the “Rosário” monthly, where he had been working since 1909. By the late 1930s, Pedro Correia Marques headed “A Voz,” the most widely read daily newspaper in Portugal.
- Trofim Danieluk

awarded
Trofim Danieluk
(1880–1960)“Upon realizing the danger I was in, Ifled and hid among potato shoots. I owe my life to Trofim Danieluk, who said I hadn’t been home for the last three days, when asked by the murderers from the Ukrainian Insurgent Army” – reported Władysław Zubkiewicz.
- Aristides de Sousa Mendes do Amaral e Abranches

awarded
Aristides de Sousa Mendes do Amaral e Abranches
(1885–1954)In the first months of the Second World War, Bordeaux in southern France seemed like a safe place – deep behind the front, far from the border of the Third Reich.
- César de Sousa Mendes do Amaral e Abranches

awarded
César de Sousa Mendes do Amaral e Abranches
(1885–1955)In the 1930s, César de Sousa Mendes was at the height of his diplomatic career. He worked at missions in Africa, Europe, America and Asia. He was Portugal’s Minister of Foreign Affairs for a year.
- Elna Gistedt-Kiltynowicz

awarded
Elna Gistedt-Kiltynowicz
(1895–1982)Warsaw audiences adored her. For Elna Gistedt from Sweden, Poland became a second home when she married industrialist Witold Kiltynowicz in 1922.
- Rodzina Gorius

awarded
Rodzina Gorius
Eugène Gorius (1873–1953) ● Marie Gorius (1881–1971) ● Léon Humbert (1900–1969) ● Rosalie Eugénie Fogel Gorius (1919–2007) ● Jeanine Humbert Hermann (ur. 1934)
- Peter Fraser (1884-1950) Janet Fraser (1888-1945)

awarded
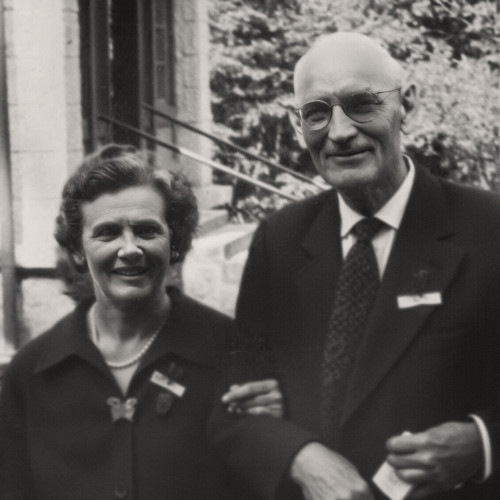
Peter Fraser (1884-1950) Janet Fraser (1888-1945)
In the autumn of 1944, the troopship USS General George M. Randall was moored at the coast of New Zealand, carrying 733 Polish children – mostly orphans – and their guardians.
- Fedor Bojmistruk (1905-1978) Kateryna Bojmistruk (1909-2000)

awarded
Fedor Bojmistruk (1905-1978) Kateryna Bojmistruk (1909-2000)
“I was crying in the barn, next to the corpses of two boys and an elderly man. I was holding a tiny piece of bread in one hand and a handkerchief with two letters in another. The letters were probably my initials.
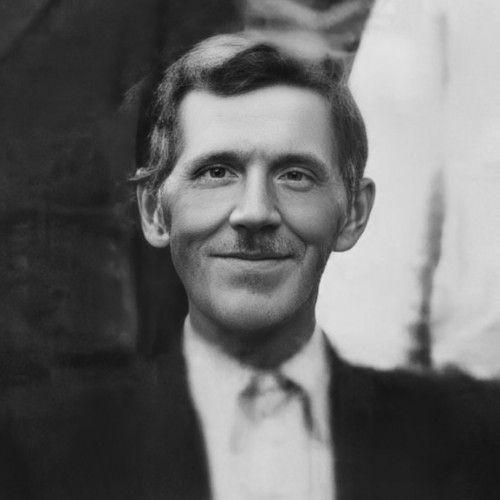
- Ján Klinovský

awarded
Ján Klinovský
(1905–1944)Ján Klinovský showed interest in Poland already as a teenager. He was from Orava, the region located at the border between Slovak and Polish cultures.
- Józsefné Margit Károlyi

awarded
Józsefné Margit Károlyi
(1892–1964)From the first days of the Second World War, many representatives of the Hungarian elite were involved in helping the Polish refugees in Hungary. One of them was Countess Margit Károlyi Józsefné.
- Skakalska, Zinaida Samczuk z d. Skakalska Musij Skakalski, Hanna Skakalska, Hanna Skakalska, Zinaida Samczuk z d. Skakalska

awarded
Skakalska, Zinaida Samczuk z d. Skakalska Musij Skakalski, Hanna Skakalska, Hanna Skakalska, Zinaida Samczuk z d. Skakalska
„In 1939, the Russians came, so we expected to be deported to Siberia [...]. Amid all this misery, we received assistance from the Skakalskis – the family of Musiy Skakalski – who were Ukrainians".
- Hélène Pionstka z d. Waldmann

awarded
Hélène Pionstka z d. Waldmann
(1921–2009)In 1941, the Germans established a POW camp for Polish soldiers close to the farm of Émile and Alice Waldmann in Ursprung, Alsace.
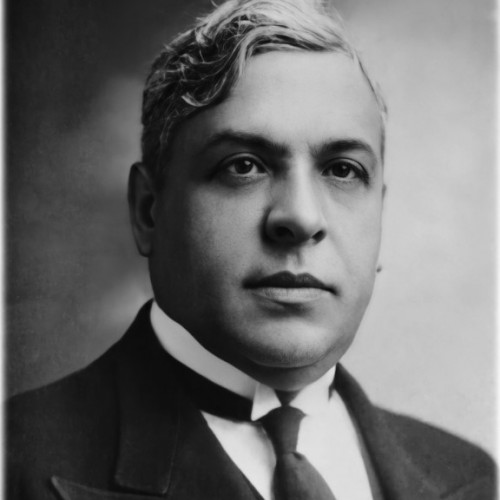
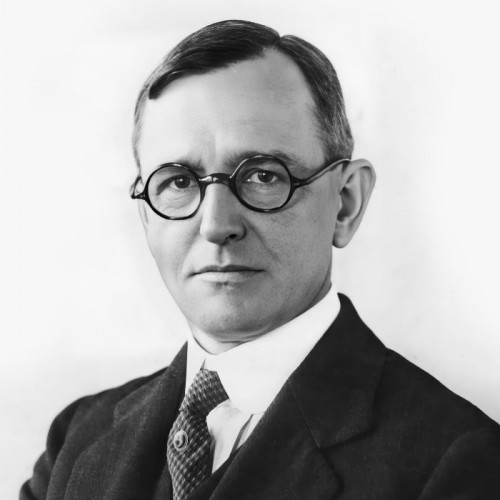
- Paul Super

awarded
Paul Super
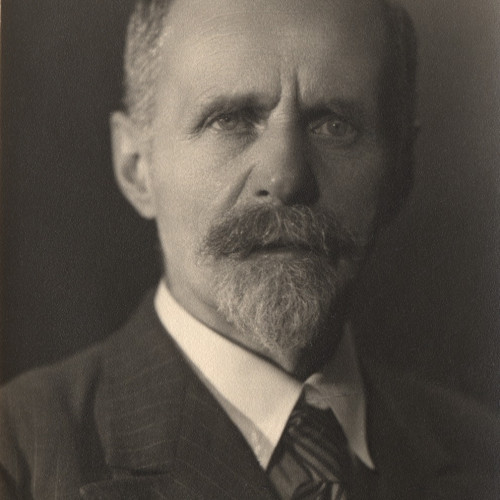
(1880–1949)Paul Super was only supposed to spend eight months in Poland. In 1922, he came to Warsaw with his family to build a local branch of the Young Men’s Christian Association (YMCA).
- Mychajło Susła

awarded
Mychajło Susła
(1901–1970)A double Christmas, a double Easter: Roman Catholic and Greek Catholic. This is how Irena Próchniak remembers the celebrations in Podkamień in eastern Galicia.
- Raymond Voegeli

awarded
Raymond Voegeli
(1894–1980)Helping those in need was the meaning of Father Raymond Voegeli’s life. Before the war, he was a member of the Camillians, whose main mission was ministering to the sick.
Awarded in 2021
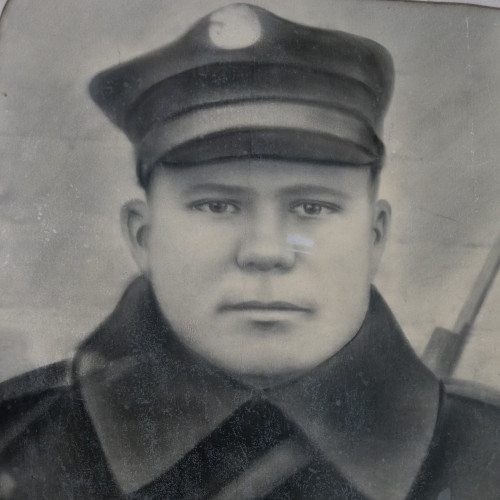
- Petro Bazeluk (1903–1949)

awarded
Petro Bazeluk (1903–1949)
Mykola Bazeluk said that there was no difference between who was a Pole and who was a Ukrainian in Volhynia before the war. That all changed in 1943, when, as he put it, “Brother turned on brother.”
- Maria Bazeluk (1903–1956)

awarded
Maria Bazeluk (1903–1956)
During the Second World War, she was living with her husband Petro Bazeluk and their three children near the village of Buteiky. The German policy that sought to take advantage of the dislike of Ukrainians for Poles was beginning to bear bloody fruit.
- Ecaterina Olimpia Caradja (1893–1993)

awarded
Ecaterina Olimpia Caradja (1893–1993)
“Kurier Polski” published in Bucharest on 3 December 1939 was full of alarming headlines: “The Soviet attack on Finland”, “Executions and deportations.” One of them gave people hope: “Under the care of Princess Caragea. Home for mothers and chilldren.”
- Jenő Etter (1889–1973)

awarded
Jenő Etter (1889–1973)
The mayor of the Hungarian city of Esztergom received dozens of letters written in Polish. The greeting lines themselves showed the sympathy and gratefulness of the Polish refugees: “Dear Captain!”, “Dear Doctor!”. Jenő Etter understood them all.
- Petro Hrudzewycz

awarded
Petro Hrudzewycz
(1939–2022)When local Soviet functionaries told him to remove the cross from the grave of soldiers of the Polish Army, he refused. However Petro was punished for his resistance, each year he attends the commemoration of the battle known as the Polish Thermopylae.
- Jan Jelínek (1912–2009)

awarded
Jan Jelínek (1912–2009)
In 1937, the care of the Evangelical parish in Kupiczów, Volhynia was entrusted to Jan Jelínek. The young pastor won the hearts of the Czechs, who had settled there in the 19th century. In his sermons he preached love of neighbor regardless of his beliefs.
- Anna Jelínková (1918–2009)

awarded
Anna Jelínková (1918–2009)
During the war the Jelíneks saved more than 40 people: the Jewish families of Fischer and Fronk, the Polish family of Siekierski, Feliks Zubkiewicz, whose loved ones were killed by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army, and the Ukrainian family of Lutsyuk.
- Jozef Lach (1905–1993)

awarded
Jozef Lach (1905–1993)
One night in October 1939, four men knocked on the door of Jozef and Žofia Lach’s home in Poprad, Slovakia. They came from the nearby Tatra Mountains, from occupied Poland.
- Žofia Lachová (1907–1979)

awarded
Žofia Lachová (1907–1979)
The courage and selflessness of Žofia and Jozef Lach helped save many Poles and ensured that the transit route to Poland was in use until almost the end of the war.
Awarded in 2019
- Tassybaj Abdikarimow

awarded
Tassybaj Abdikarimow
(1938–2020)The Jabłoński family were in an difficult situation — terrible sanitary conditions, shortage of food, and hard labor in the sun caused a very high mortality rate among he inhabitants. During this difficult time, help came from a 16-year-old Kazakh.
- Chaim Yisroel Eiss

awarded
Chaim Yisroel Eiss
(1876–1943)Cooperating with the Polish diplomats in Bern, he created a network to smuggle passports into the ghettos of occupied Poland.
- Anatolij Giergiel (1904—1981)

awarded
Anatolij Giergiel (1904—1981)
In the summer of 1943 in Volhynia, having learned about a planned attack by Ukrainian nationalists on Poles, Anatolyi Giergiel warned his friend.
- Zinaida Giergiel z d. Radczuk (1912—1989)

awarded
Zinaida Giergiel z d. Radczuk (1912—1989)
Zinaida Giergiel suspected that after being chased out of their homes and suffering from hunger, the Poles would attempt to return to their farms. She was able to warn polish family that a unit of the OUN/UPA was waiting for them in the house.
- prof. Władysław Konopczyński (1880—1952)

awarded
prof. Władysław Konopczyński (1880—1952)
After the Warsaw Uprising, among the crowds expelled from the burning city were the family of a Polish-Jewish historian, Ludwik Widerszal. Konopczyński offered shelter in Młynik until the end of the war.
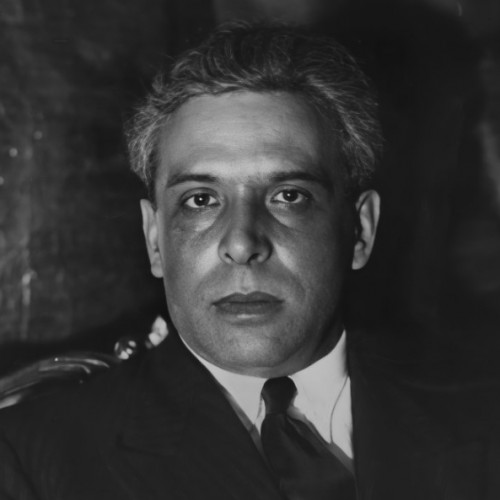
- dr Juliusz Kühl (1913—1985)

awarded
dr Juliusz Kühl (1913—1985)
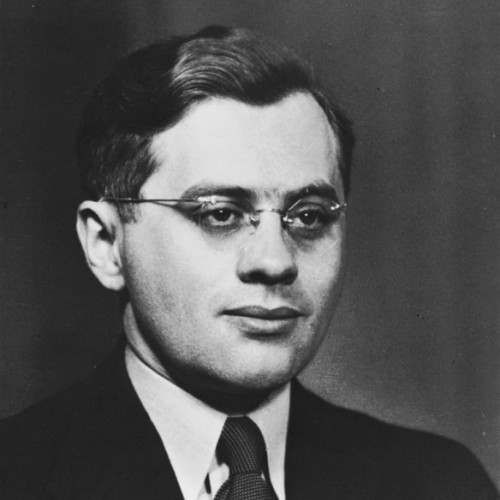
As a member of the Ładoś Group, he was responsible for acquiring Latin American passports in blanco and for contacting Jewish organizations.
- Antoni Nagórka (1901—1977)

awarded
Antoni Nagórka (1901—1977)
Antoni and Władysława Nagórka lived at the edge of the town. Before the war, Antoni worked for the railways, and Władysława was a housewife. During the war they saved five Jews from the Holocaust.
- Władysława Nagórka z d. Lech (1895—1981)

awarded
Władysława Nagórka z d. Lech (1895—1981)
Antoni and Władysława Nagórka lived at the edge of the town. Before the war, Antoni worked for the railways, and Władysława was a housewife. During the war they saved five Jews from the Holocaust.
- Konstanty Rokicki (1899—1958)

awarded
Konstanty Rokicki (1899—1958)
Rokicki was responsible for one of the Ładoś Group’s most important tasks. In the years 1941—1944 he alone hand-wrote several thousand Paraguayan passports.
- Stefan Jan Ryniewicz (1903—1988)

awarded
Stefan Jan Ryniewicz (1903—1988)
He was the deputy to Aleksander Ładoś. Ryniewicz’s role was to provide diplomatic security to the whole operation.
- Abraham Silberschein (1881—1951)

awarded
Abraham Silberschein (1881—1951)
He was a member of the Ładoś Group, which issued illegal Latin American passports to European Jews. His role in the group was to provide lists and photographs of people who were to receive the passports.
- gen. Lóránd Utassy (1897— 1974)

awarded
gen. Lóránd Utassy (1897— 1974)
Utassy denied the Gestapo access to the internment camps and refused to surrender Polish soldiers. He also participated in talks with the Red Cross, aiming to establish it as the representation of Poles who had found themselves on Hungarian soil.
- Ołeksandra Wasiejko z d. Łukaszko (ur. 1946)

awarded
Ołeksandra Wasiejko z d. Łukaszko (ur. 1946)
During the Volhynia Massacre in the summer of 1943. Over the next seventy years Oleksandra Vaseyko kept alive the memory of the victims, bringing flowers to their graves and keeping them in her prayers.
- Aleksander Ładoś (1891-1963)

awarded
Aleksander Ładoś (1891-1963)
He was the leader of the group which issued illegal Latin American passports to persecuted Jews. Ładoś gave the group diplomatic protection.