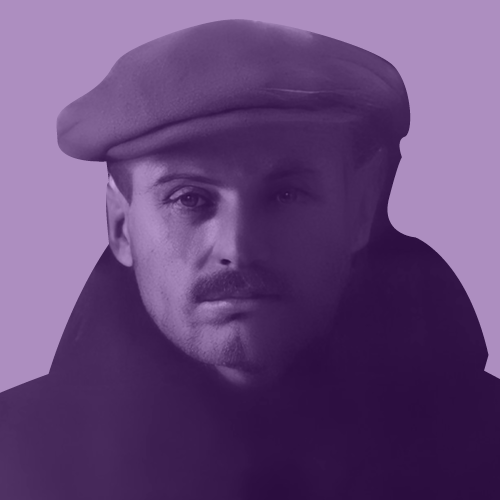
Jozef Lach (1905–1993) - Instytut Pileckiego
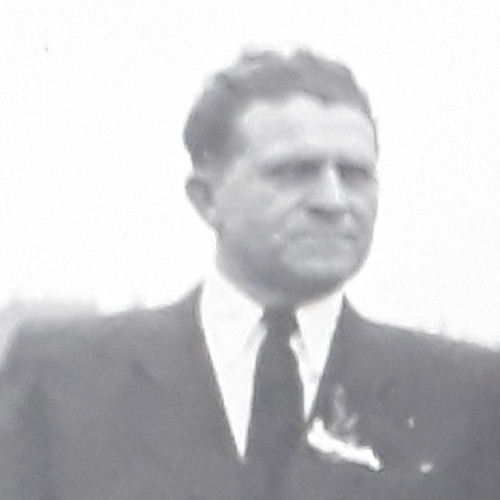

One night in October 1939, four men knocked on the door of Jozef and Žofia Lach’s home in Poprad, Slovakia. They came from the nearby Tatra Mountains, from occupied Poland.
They gave Jozef a letter from his good friend, Jozef Kertész, asking Lach, a taxi driver, to transport the Polish airmen to the Hungarian border. This is how Lach started to help Poles who wanted to get to Hungary through Slovakia. The number of refugees was growing so fast that he recruited other taxi drivers to help. Soon he started transporting couriers and underground activists in the opposite direction – towards the Polish border. He also obtained forged Slovak documents for his passengers.
While Jozef took charge of the transport, his wife Žofia set up a hideout in their house. Despite having children, they risked getting arrested by the Slovak authorities who were subordinate to the Germans and continued to give shelter to Polish refugees, treating them like their own family.
With time, the Lach family gained the trust of Józef Krzeptowski – the “king of the Tatra couriers.” When his wife, father-in-law and brother-in-law were in danger of getting arrested by the Germans, Jozef Lach transported them across the border to Poprad, where they survived by hiding in the Lachs’ house for several months. The Poles would call their house a “hotel for couriers.”
Jozef was captured only once, in the summer of 1943, when Slovak gendarmes cut him off on the road near the village of Veľká Franková. His Polish passengers and the British agent whom they were escorting managed to jump out of the taxi and escape, but Jozef and his son were arrested. They were released only thanks to the kindness of the commandant who decided not to hand them over to the Gestapo.
The courage and selflessness of Jozef and Žofia Lach helped save many Poles and ensured that the transit route to Poland was in use until almost the end of the war. The Lachs were later nominated for a number of Polish decorations, but Communist Czechoslovakia refused to back this effort.
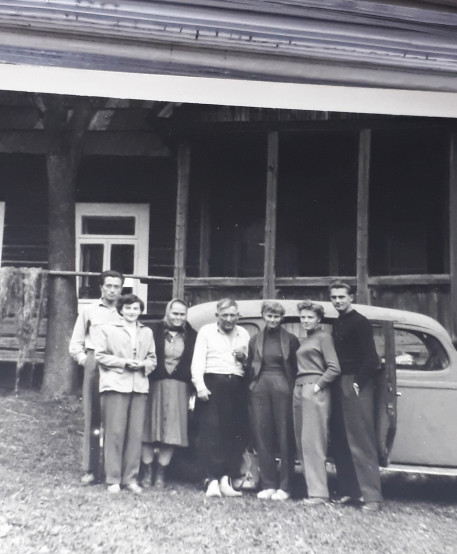

I successfully crossed the border and went around Betliar and Poloma. When I came out of the woods, Lach was already waiting for me. The taxi ride was awful, but Jozef skillfully dealt with the snow drifts.
Memoirs of Zbigniew Ryś
See also
- Aud Valla

awarded
Aud Valla
(1922–2014)Aud Sejlelid, still going by her maiden name at the time, spent her entire life in the small town of Hemnesberget in northern Norway, in a picturesque land of fjords.
- Semen Biliczuk

awarded
Semen Biliczuk
(1890–1944)Jews, Ukrainians, Poles – the population of the prewar village of Kisielin [now Kysylyn] [now Kysylyn] was characterized by a vivid mosaic of ethnic and religious groups. The leader of such a community had to be able to find a common ground with everyone.
- Martha Gammer (1947)

awarded
Martha Gammer (1947)
In the 1970s, few people knew that the tunnels excavated in the hills near Gusen were the result of slave labor by prisoners of the German Nazi concentration camp that existed there during the Second World War.