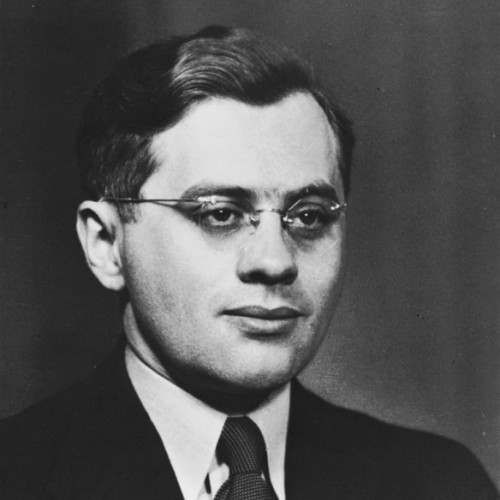
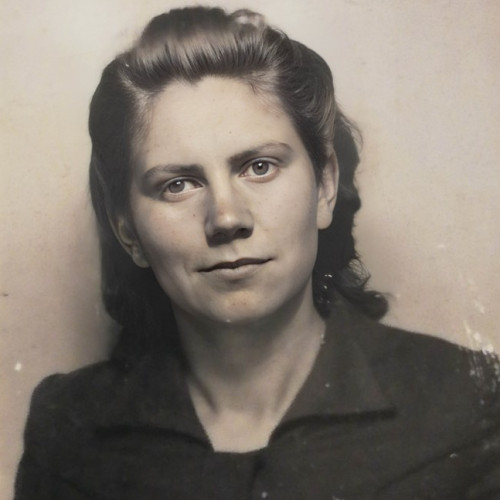
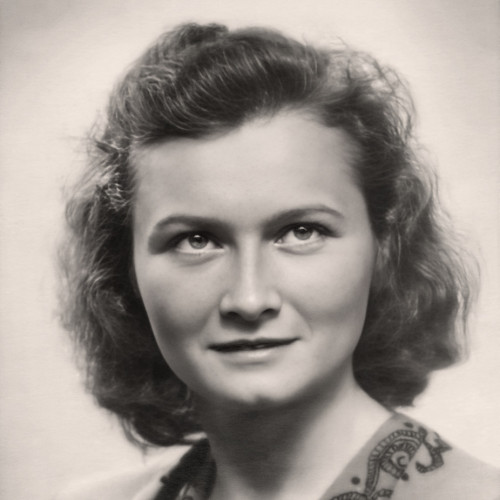Maria Bazeluk (1903–1956) - Instytut Pileckiego

During the Second World War, she was living with her husband Petro Bazeluk and their three children near the village of Buteiky. The German policy that sought to take advantage of the dislike of Ukrainians for Poles was beginning to bear bloody fruit.
The Bazeluks heard the news of the massacres of Polish villages in Volhynia that had been carried out by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army.
During the Second World War, she was living with her husband Petro Bazeluk and their three children near the village of Buteiky. The war had been raging for four years already, and the German policy that sought to take advantage of the dislike of Ukrainians for Poles was beginning to bear bloody fruit. The Bazeluks heard the news of the massacres of Polish villages in Volhynia that had been carried out by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army.
In July 1943, the village of Huta Stepańska fell victim to Ukrainian Insurgent Army, and the wife of Mieczysław Słojewski was killed in the massacre. Mieczysław and his son Edward survived and fled to the forest to hide. The growing cold, hunger and fear of the Ukrainians drove them to their limits.
In November 1943, the Słojewskis happened upon an old acquaintance in the forest, Petro Bazeluk. The Poles were terrified of the man with the ax in his hand, and Petro said to Mieczysław, “Don’t be afraid, come with me.” Bazeluk and his wife Maria hid the Poles in their barn, where they lived from November 1943 until April 1944.
The Bazeluks were risking not only their own lives, but the lives of their children as well. The Słojewskis were never discovered, however, despite numerous searches of the property by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army. The Bazeluks gave their refugees security and a semblance of a home; Maria taught Mieczysław and Edward how to knit, thus enabling them to make their own gloves, socks and jumpers for themselves and for their carers.
After the war, the Słojewskis moved to Lower Silesia. Petro Bazeluk remained in Buteiky, where he was shot in 1949 by a Soviet official for refusing to comply with forced collectivization.
Petro Bazeluk almost used force to lead the father and the son to his home under cover of darkness. When Petro’s wife learned of their misery and suffering, she began to weep and took them in with open arms.
Account of Władysław Kurkowski
See also
- Aud Valla

awarded
Aud Valla
(1922–2014)Aud Sejlelid, still going by her maiden name at the time, spent her entire life in the small town of Hemnesberget in northern Norway, in a picturesque land of fjords.
- dr Juliusz Kühl (1913—1985)

awarded
dr Juliusz Kühl (1913—1985)
As a member of the Ładoś Group, he was responsible for acquiring Latin American passports in blanco and for contacting Jewish organizations.
- Hélène Pionstka z d. Waldmann

awarded
Hélène Pionstka z d. Waldmann
(1921–2009)In 1941, the Germans established a POW camp for Polish soldiers close to the farm of Émile and Alice Waldmann in Ursprung, Alsace.