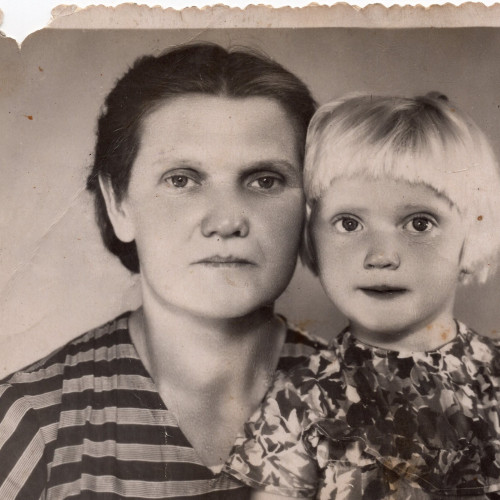Anna Jelínková (1918–2009) - Instytut Pileckiego

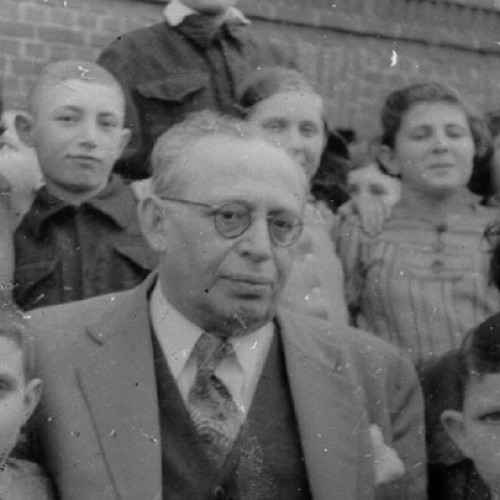
During the war the Jelíneks saved more than 40 people: the Jewish families of Fischer and Fronk, the Polish family of Siekierski, Feliks Zubkiewicz, whose loved ones were killed by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army, and the Ukrainian family of Lutsyuk.
In 1937, the care of the Evangelical parish in Kupiczów, Volhynia was entrusted to Jan Jelínek. The young pastor quickly won the hearts of the local Czechs, who had settled there in the 19th century. In his sermons he preached love of neighbor regardless of his nationality, religion and beliefs. These were not obvious teachings with Europe facing the threat of war. When it eventually broke out, Jelínek practiced what he preached – he modeled himself on the Good Samaritan.
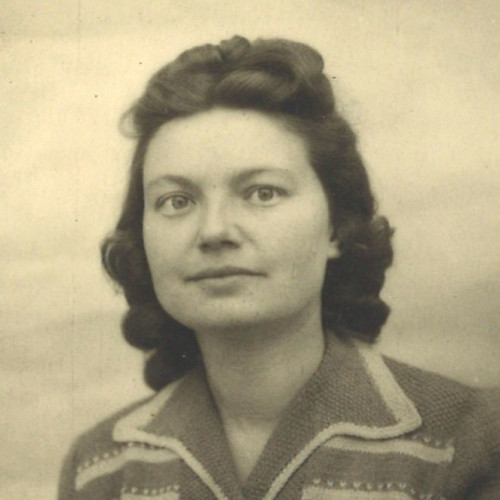
As early as in 1939, the pastor provided shelter for Polish soldiers who were fleeing Soviet occupation to Romania. When the Germans replaced the Soviets as the occupying power, Jelínek engaged in helping the Jews – he hid them in his house and brought food to the ghetto in Kowel. “I was helping a human being,” he once said in response to a German officer who threatened him with death for rescuing Jews. Jelínek was supported in his activities by his wife Anna, whom he married in 1942.
During the Volhynia Massacre they gave shelter to Poles from the villages attacked by Ukrainian nationalists. Jelínek’s example was followed by his Czech parishioners, and thus Kupiczów became a haven for many Poles fleeing the Ukrainian Insurgent Army. When in 1944 the Germans were repelled by the Soviets, Jelínek issued false birth certificates to people in danger of arrest by the NKVD.
During the war the Jelíneks saved more than 40 people in total, mostly citizens of the prewar Poland: the Jewish families of Fischer and Fronk, the Polish family of Siekierski, Feliks Zubkiewicz, whose loved ones were killed by the Ukrainian Insurgent Army, and the Ukrainian family of Lutsyuk.
The Jelíneks left Volhynia with the Czechoslovak Army Corps that fought alongside the Red Army. After the war they settled in Oráčov in western Czechoslovakia. Jan was persecuted for his beliefs by the communist authorities, and as a result his health deteriorated, but both spouses lived to a ripe old age.
Dear Reverend Father, on this momentous and festive occasion I would like once again to express my heartfelt gratitude for the help that you had offered our family at the time of inhumane barbarity of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army bands in Volhynia. Such humane gestures are never forgotten! Respectfully Yours
Letter from Halina Siekierska-Ligęza to Jan Jelínek on the occasion of his 90th birthday, 2002
See also
- Zinaida Giergiel z d. Radczuk (1912—1989)

awarded
Zinaida Giergiel z d. Radczuk (1912—1989)
Zinaida Giergiel suspected that after being chased out of their homes and suffering from hunger, the Poles would attempt to return to their farms. She was able to warn polish family that a unit of the OUN/UPA was waiting for them in the house.
- Wołodymyr Kryżuk

awarded
Wołodymyr Kryżuk
Since the early 2000s, he has been helping Poles who travel to look after the graves of the victims of the massacre carried out by members of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army (faction of the Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists).
- Abraham Silberschein (1881—1951)

awarded
Abraham Silberschein (1881—1951)
He was a member of the Ładoś Group, which issued illegal Latin American passports to European Jews. His role in the group was to provide lists and photographs of people who were to receive the passports.