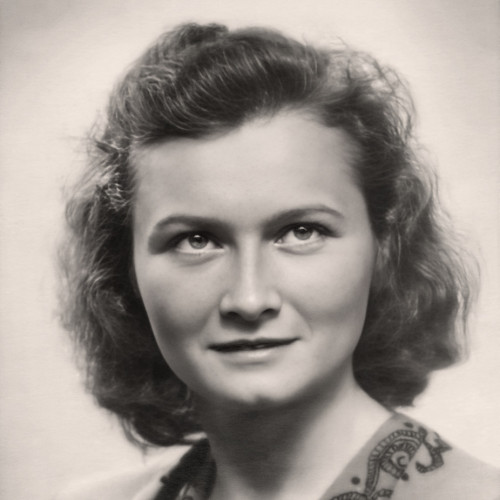Ecaterina Olimpia Caradja (1893–1993) - Instytut Pileckiego

“Kurier Polski” published in Bucharest on 3 December 1939 was full of alarming headlines: “The Soviet attack on Finland”, “Executions and deportations.” One of them gave people hope: “Under the care of Princess Caragea. Home for mothers and chilldren.”
The article described the fate of the children of Polish refugees in Romania – “small, petite, innocent children, who were forced to roam since the very beginning of their lives.” Fortunately, “they found a kind guardian” – Princess Ecaterina Olimpia Caradja.
The Romanian aristocrat and philanthropist was head of the charitable Association of Saint Catherine’s Cribs. On 24 September 1939, she provided Polish families in Bucharest with access to two buildings, including a spacious pavilion, with nurseries, playrooms and a reading room for children. The youngest received four meals a day. A Polish school was established right away. The establishment provided refuge to 120 Poles. As a representative of the International Committee for Children’s Relief, Caradja also distributed clothes for children among other refugee communities.
The princess often intervened with the Romanian authorities to provide greater support to the Polish refugees. She collaborated with Paul Super, who supervised the American aid to Poles in Romania. While some of the refugees left Romania for other countries before the end of the war, the rest returned to Poland in 1945.
In 1952, Caradja was forced to flee from communist Romania to the United States. She returned to her homeland shortly before her death. On account of her support for the Allied soldiers who had been taken prisoner, she was referred to as the “Angel of Ploiești.” She was also an “angel” to the Polish children. “Kurier Polski” described her as having “great energy, an unfailing smile, a kind word for everyone, and a willingness to compassionately hear out everyone’s struggles.”
Princess Caragea cooperated with us with great devotion, looking after infants, children and women. Her remarkable personal qualities, energy and readiness to collaborate have made her one of the most exceptional individuals in the entire relief campaign.
Report by Paul Super, director of the American Commission for Polish Relief in Hungary and Romania to the Ministry of Military Affairs, 1940
See also
- Antoni Nagórka (1901—1977)

awarded
Antoni Nagórka (1901—1977)
Antoni and Władysława Nagórka lived at the edge of the town. Before the war, Antoni worked for the railways, and Władysława was a housewife. During the war they saved five Jews from the Holocaust.
- Aud Valla

awarded
Aud Valla
(1922–2014)Aud Sejlelid, still going by her maiden name at the time, spent her entire life in the small town of Hemnesberget in northern Norway, in a picturesque land of fjords.
- Chaim Yisroel Eiss

awarded
Chaim Yisroel Eiss
(1876–1943)Cooperating with the Polish diplomats in Bern, he created a network to smuggle passports into the ghettos of occupied Poland.